

I’d imagine mpd with one of many frontends would work well enough. You’d just need to use a dummy music library directory with symlinks to your four music storages for mpd to pick up and catalog everything.


I’d imagine mpd with one of many frontends would work well enough. You’d just need to use a dummy music library directory with symlinks to your four music storages for mpd to pick up and catalog everything.
Tbf to cloud sync, nothing is stopping you from using your own backup/restore service with your drm-free titles compared to the other features that Galaxy offers.
GOG has DRM for many titles: see Galaxy. As I understand it, it isn’t as pervasive as Steam, but is necessary if you want multiplayer on many titles or care about extras like achievements.
On my Fedora KDE install on 40, hibernate is now an available power option. The install has been in upgrade cycles since 35 at this point. I would imagine that barring different DEs showing different power options being a possibility, it is more on detecting hardware compatibility for functional hibernation.
Tiny 11 comes in two variants:
Tiny11 Core is not suitable for use on physical hardware as it outright disables updates. It’s best used for short-term VM instances.
Tiny11 also has problems with updates. The advantages gained through Tiny11 will erode with applying Windows updates. The installer is more tolerable than Windows 11 by not forcing an online account (but still needing to touch telemetry settings). Components like Edge and One drive will inevitably rebuild themselves back in with cumulative updates. If this is something that coerces you to not update your system, don’t subject yourself to using Tiny11. Additionally Tiny11 fails to apply some cumulative updates out of the box, which could be a further security risk.
I recently tested the main Tiny11 in a VM based on a different user recommending it in a now deleted thread. I was skeptical knowing the history of Tiny10 onward that 11 would actually be able to update properly, and NY findings backed up my initial skepticism of functional updates.
Use the OCI through podman or docker.
The heated bed is coupled to a thermistor. I’d argue controlling the temperature in order to not accidentally overheat parts of the phone is a step above a hair dryer.
What compositor (desktop environment) and distro are you running for things to behave that poorly?
The worst gotchas and limitations I have seen building my own self-host stack with ipv6 in mind has been individual support by bespoke projects more so system infrastructure. As soon as you get into containerized environments, things can get difficult. Podman has been a pain point with networking and ipv6, though newer versions have become more manageable. The most problems I have seen is dealing with various OCI containers and their subpar implementations of ipv6 support.
You’d think with how long ipv6 has been around, we’d see better adoption from container maintainers, but I suppose the existence of ipv6 in a world originally built on ipv4 is a similar issue of adoption likewise to Linux and Windows as a workstation. Ultimately, if self-rolling everything in your network stack down to the servers, ipv6 is easy to integrate. The more one offloads in the setup to preconfigured and/or specialized tools, the more I have seen ipv6 support fall to the wayside, at least in terms of software.
Not to mention hardware support and networking capabilities provided by an ISP. My current residential ISP only provides ipv4 behind cgnat to the consumer. To even test my services on ipv6, I need to run a VPN connection tunneling ipv6 traffic to an endpoint beyond my ISP.
If that is the case, the developer should have likely noted otherwise before closing the issue as the final piece of discussion. That is good to know that your experience hasn’t dropped the OS into base Windows 11. If as you say is true, the developer should also really spend some time cleaning up the README and clarify that base Tiny11 can actually be updated in-OS. I will still test in a VM later today to confirm that Tiny11 doesn’t actually erode or degrade on update for myself.
From the Github README:
Also, for the very first time, introducing tiny11 core builder! A more powerful script, designed for a quick and dirty development testbed. Just the bare minimun, none of the fluff. This script generates a significantly reduced Windows 11 image. However, it’s not suitable for regular use due to its lack of serviceability - you can’t add languages, updates, or features post-creation. tiny11 Core is not a full Windows 11 substitute but a rapid testing or development tool, potentially useful for VM environments.
It literally says that it cannot be updated from a built OS install. You need to reinstall tiny11 by rebuilding the install image with a newer Windows 11 base image. Obviously it would be best to do this every time there is a security patch release for Windows 11.
EDIT: Rereading further, the bigger Tiny11 image might be able to be updated in-OS. I’m going to dig through the ps1 scripts to see if the README holds up to that un-noted capability.
EDIT2: I don’t see any registry edits that knock Windows Updater offline. I’ll test it in a VM to see if things work (from prebuilt when it eventually downloads). Though I am unsure at this moment if such an image’s changes will survive a Windows update at all.
EDIT3: VM not tested yet, but an issue on the GitHub seems to corroborate my initial assumption.
EDIT4: VM tested. Things claimed to be patched out (Edge) came back with one of the cumulative updates applied shortly after install. Other cumulative updates are being blocked (error instantly on attempt to install after download) (perhaps unintentionally). Image downloaded claimed to be for 23H2, but Windows 11 22H2 was installed, seemingly with no way to actually upgrade. I think my point stands.
Do note that this system is liable to leave your computer vulnerable as it has no way to update itself from within the OS.
This image would be fine for booting short-term VMs as long as you periodically rebuild and reinstall it, but not ready for consumer use.
Windows does have memory compression, though you can’t really change the algorithm or how aggressive it is. AFAIK it is just a toggle of on or off.
Beyond the article being ancient at this point (in terms of AOSP and Android development lifetime), Stallman’s argument boils down to the same talking points of Free Software purism.
To the first real point being transformed here: Android is not GNU/Linux because it does not contain much of the GNU Project’s software. While it’s correct to claim it’s not GNU/Linux, how does it not make it Linux still? Is Alpine Linux not considered “Linux” because it doesn’t contain GNU? Please elaborate on this point of Linux being Linux because it has GNU.
To the second point of including proprietary drivers, firmware, and appplications: we once again meet the questionable argument of transforming an OS to something else. Points are made that Android doesn’t fit the GNU ideals due to its usage and inclusion of proprietary kernel modules, firmware, and userland applications. These are valid points to be made in that these additions muddy the aspect of Android (as packaged by Google and major smartphone manufacturers) being truly free software. However the same can be said about traditional “GNU/Linux distributions”. Any device running on x86 (Intel, AMD) will be subject to needing proprietary firmware in order to function with that firmware having a higher control level than the kernel itself, just as Android would. There is also the note that while it is less necessary now to have a functioning desktop, a good portion of hardware (NVidia, Broadcom, Intel, etc.) require proprietary kernel modules and/or userland drivers in order to have full functionality that the average user may want. Finally, there is proprietary applications as well. Some Linux desktops include proprietary applications like Spotify, Steam, Google Chrome by default. Are we really to also exclude an overwhelming majority of the biggest Linux distros as Linux as well being that they include proprietary software or rely on proprietary code in some fashion? GNU itself lists very few distros as GNU-approved.
To note, AOSP does have a different userland environment than your standard Linux distro running X11 or Wayland. That is by far the best reason I could think of to classify Android as a different category of ‘Linux’ from say Debian, Fedora, OpenSUSE, Arch, Gentoo, Slackware, and others. However, AOSP is still capable of running with no proprietary userland software and can even be made to still run cli applications as well as run an X11 server that is capable of launching familiar desktop Linux applications. I really think that the arbitrary exclusion of Android from being Linux by virtue that RMS doesn’t think it fits with GNU ideals is silly. If there are better arguments to be said for why Android (especially AOSP) shouldn’t be seen as Linux with a different userland ecosystem rather than not Linux entirely, I’d love to see them. However, I remain unconvinced so far.
The A485 is actually such a terrible laptop. I would never reccomend such garbage to anyone considering mine almost never worked properly. I had in three years have six main board replacements for various hardware faults. Not a single of the boards has been free from severe hardware faults.


I have been utilizing BunkerWeb for some of my selfhost sites since it was bunkerized-nginx. It is indeed powerful and flexible, allowing multi-site proxying, hosting while allowing semi-flexible per-site security tweaks (some security options are forcibly global still, a limitation).
I use it on podman myself, and while it is generally great for having OWasp CRS, general traffic filtering targets and more built on top of nginx in a Docker container, the way Bunkerweb needs to be run hasn’t really remained stable between versions. Throughout several version upgrades, there have been be severe breaking changes that will require reading the setup documentation again to get the new version functional.


I just did some testing in the past hour or so and did a portable install from scratch using the Fedora Workstation 39 iso. I’m not exactly sure what your hardware detection issue would have been, but I can say that Anaconda could detect both a USB flash drive and an external hard drive I had plugged in.
Going with the USB flash drive, I did skip using the automatic partitioning and went for using blivet to do my work. I did format the drive beforehand as I have always had issues with that drive properly accepting various partitioning commands (the installer no exception as tested). I did reserve a partition for a shared storage filesystem, but didn’t actually give it a filesystem here.
In blivet, here is a sample of the kind of partition schema I was talking about (something that might be helpful to OP or anyone else that wants to try this setup):
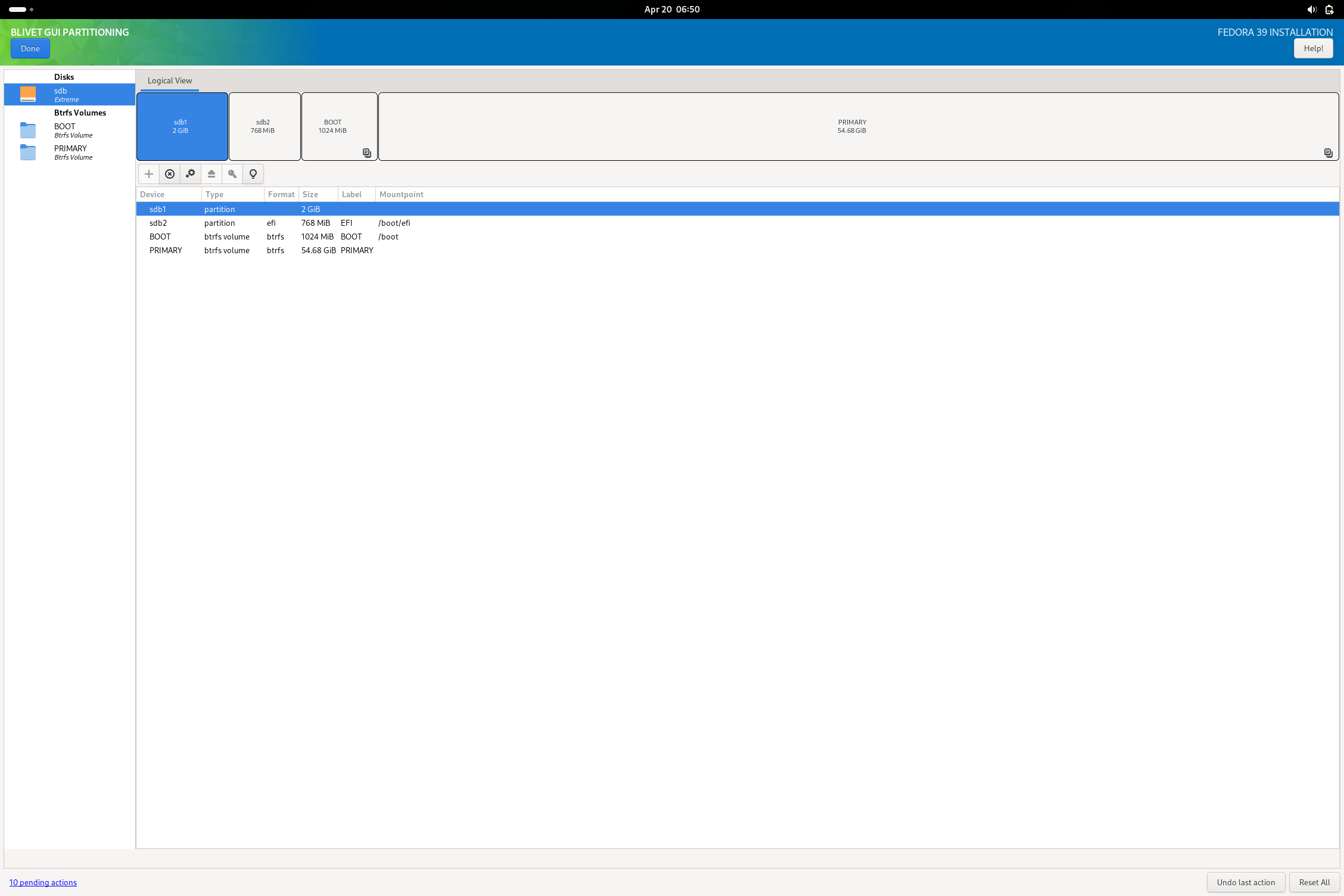
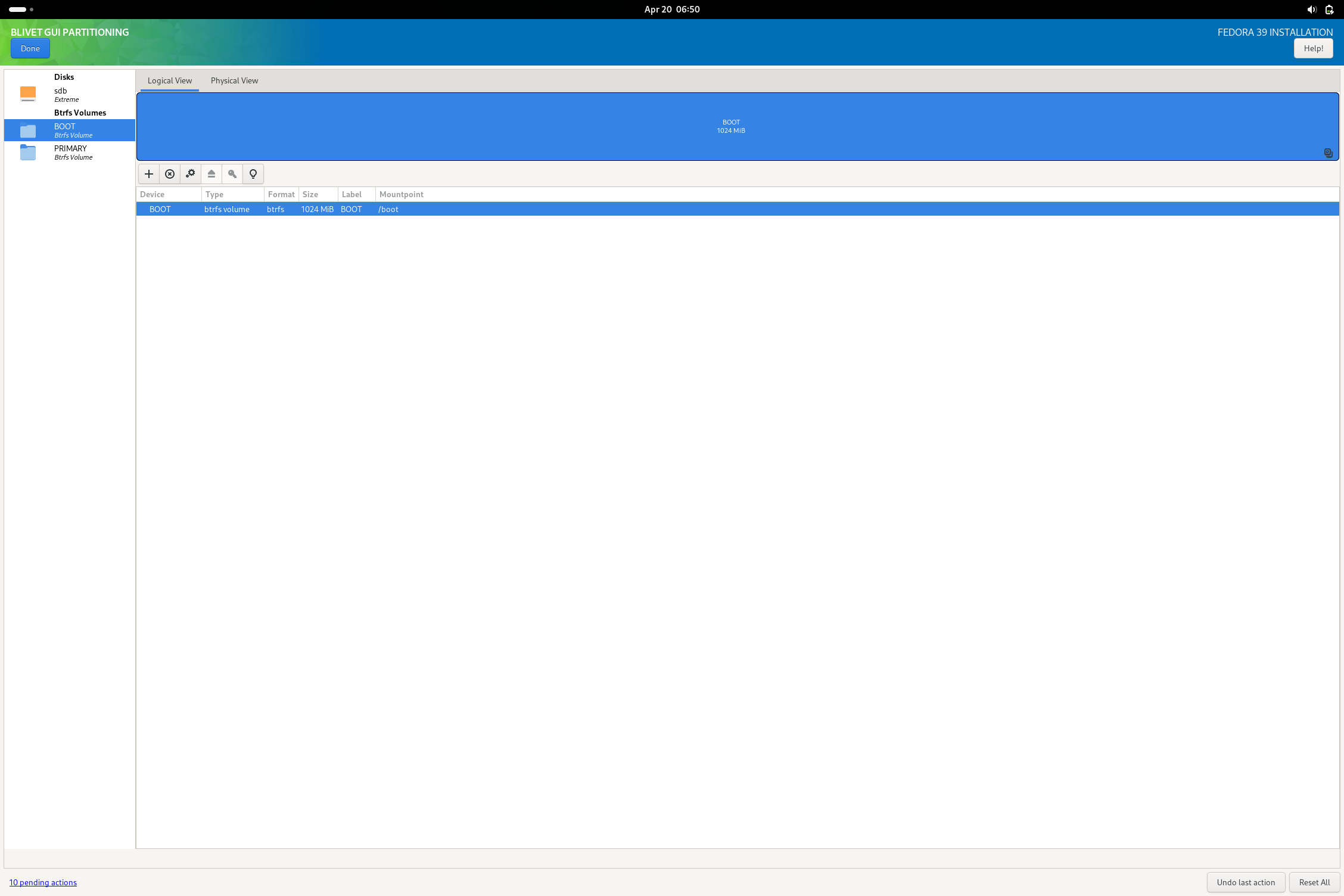
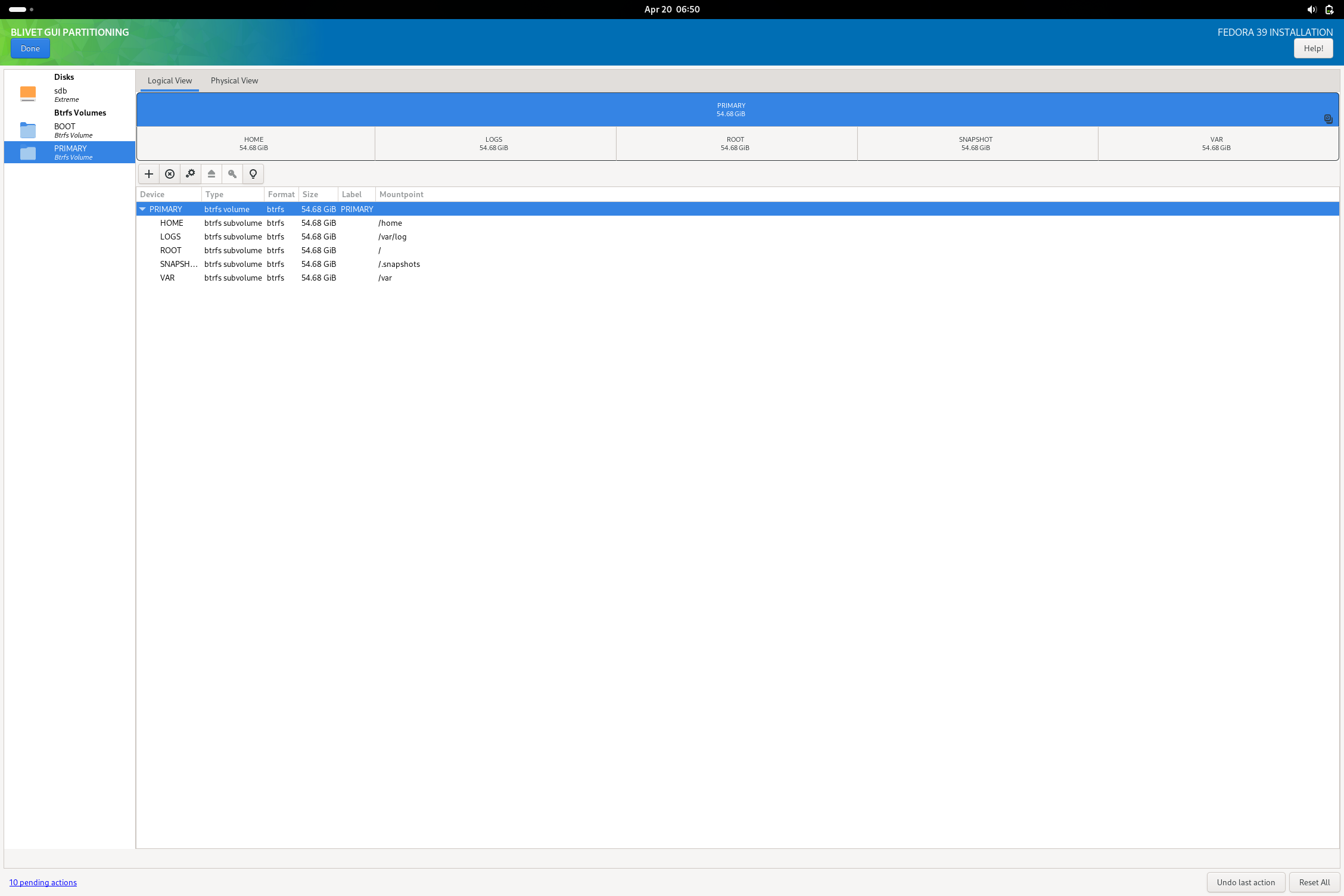
I was able to then complete the install as normal and boot into the finished USB drive. I noted a small non-fatal complaint from grub on boot, but I imagine this is fixed with updating the system. All systemd units boot without failure and I am able to get the system working with minimal issue. The only real issue I could note is that the installation is very sluggish (due to it being on a flash drive rather than an external ssd or some other more suitable media). After booting, I then opened Disks and added the missing exfat (or NTFS) filesystem I reserved a partition for. The reason I didn’t do this in blivet during install is because the option doesn’t actually exist to make an exfat fs in the tool.
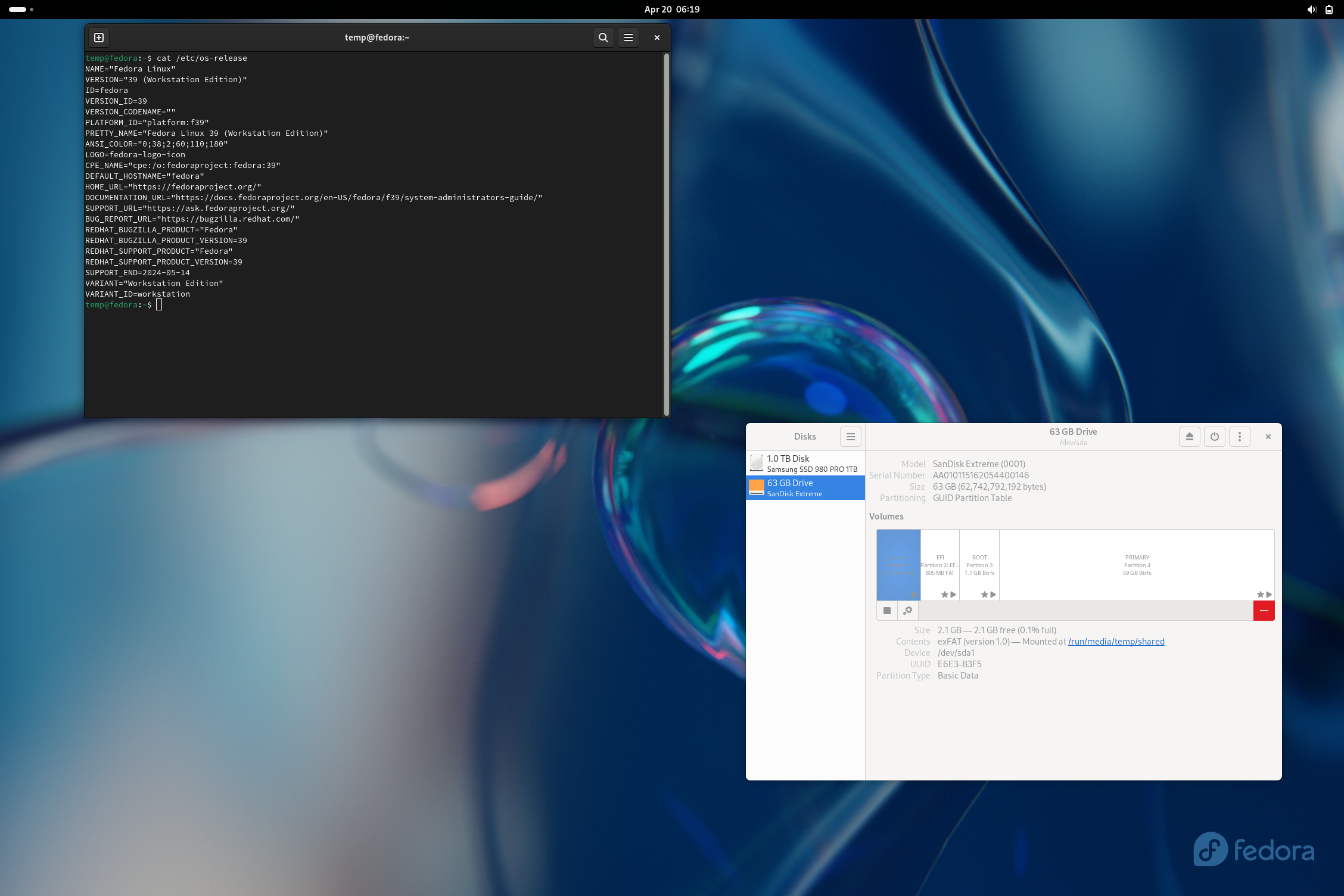
Hopefully, this comment is helpful toward getting such a setup working.
EDIT:
Something I did notice with GRUB on Fedora Workstation 39 is that by default, the menu will not show unless pressing escape on boot. There is a useful AskUbuntu post that explains in detail how to access the grub menu and how to change it to behave in a better fashion for a multiboot system.


Ah, that would put a bit of complication into things. If you want to actually accomplish this though, you should largely start with the same steps as a standard system install, using a second USB flash drive to write the distro onto the external SSD, leaving enough space to build the rest of the partitions you need. If you intend to make a Windows-shared partition (exfat, fat32, or NTFS), it is probably best to put that partition either first or just behind the EFI partition so that Windows systems won’t have a hard time finding it. Exfat or NTFS would be a better choice for this type of partition.
I would still generally recommend keeping the live distros on a separate bootable drive, but you can size and reserve dummy partitions after the rest of your normal dual-boot installs and shared data partitions for live installers to overwrite. There is likely going to be some experimentation with getting the OS bootloader (such as on GRUB provided by Fedora in this case) to pick them up and add them as boot entries. You should (depending on the live image) be able to dd write them to the ending partitions reserved for the image for as long as the partition is sized equal or larger than the ISO image’s size (it’s best to give at least a few blocks of oversize on the partition when writing ISO’s directly).
Edit: In a proper Fedora install, you should almost never need to disable selinux or set it to permissive unless you know why you don’t want it.


For the longest time reading this post, I didn’t catch that you were setting up a simple dual boot for an internal SSD and thought with using tools like Ventoy you were making a multiboot portable install.
You are obscenely overcomplicating this. Your current approach is almost completely wrong to getting a functional multiboot system that passes secure boot and everything else.
Quite literally, bootstrapping from windows can use Rufus or ventoy on a USB stick to dump the ISOs on. Then boot into bios from the USB EFI entry. From there, simply install Fedora (no VM necessary). You’ll get Fedora installed in a GPT/EFI configuration (if you formatted your drive for install). If doing manual partitioning to leave space or do other configurations, format the drive to GPT. If multibooting, you may want to expand your EFI partition beyond 512MiB for multiple distros.
For other Linux OS to install alongside, you can then install them in the free space. Another comment mentioned to not install a bootloader on the secondary OS(es), which is generally a good idea.
For Tails, it is not meant to be installed on an SSD. It is best to use it on a flash drive.
Overall, a majority of your issues stem from the following:
I’d argue your conclusion of people not switching to Linux because you found it too hard is almost entirely not because of any issue on Linux, but the factors you wedged yourself into on a modern x86 PC due to your methods in accomplishing your goal.
What makes Nextcloud unreliable for your use case? I’ve used the calendar (caldav) functionality for years without issue in sync.